Curious about how air-source heat pumps work in winter?
We explore the components of an air source heat pump and the benefits of using one during the colder months.
Learn how these systems provide energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly heating. We will also discuss the factors that can affect the performance of an air source heat pump in winter, as well as tips for maintaining and troubleshooting these systems.
Stay tuned to learn more!

What Is An Air Source Heat Pump?
An air source heat pump is a highly efficient system that transfers heat from the outside air to your home, even in cold weather, making it a reliable option for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the winter.
There are two main types of air-source heat pumps: air-to-air and air-to-water. Air-to-air pumps transfer heat from the outside air into your home using fans and ducting systems. On the other hand, air-to-water pumps transfer heat to a water-based system which can then provide heating through underfloor heating systems or radiators.
These heat pumps work by extracting heat from the outdoor air, even when temperatures drop below freezing. They do this by utilising a refrigerant that absorbs heat from the air and then compresses it, raising the temperature. This heat is then transferred into your home through a distribution system, providing efficient heating even in chilly conditions.
Efficiency is a key advantage of air source heat pumps, as they can generate more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume. This makes them a cost-effective and sustainable heating solution, especially with their ability to operate effectively in varying temperatures.
Gain insights: What Is An Air Source Heat Pump

How Does An Air Source Heat Pump Work?
An air source heat pump works by absorbing heat from the outside air and transferring it indoors, effectively heating your home even in winter conditions, thanks to its high efficiency and advanced technology.

What Are The Components Of An Air Source Heat Pump?
The main components of an air source heat pump include the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve, all working together to provide efficient heating for your home.
Let’s start with the evaporator. This component is responsible for absorbing heat from the surrounding air, acting as the starting point of the heat transfer process. Once the refrigerant within the evaporator captures this heat energy, it transitions to the compressor.
The compressor plays a critical role in the system by pressurising the refrigerant gas and increasing its temperature and energy level. This high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser, where it releases the absorbed heat to the indoor space, thereby heating it effectively.
Next comes the expansion valve, which regulates the flow of the refrigerant, controlling its pressure and temperature. This component ensures that the refrigerant reaches the evaporator at the optimum conditions for efficient heat absorption, completing the cycle.

What Are The Benefits Of Using An Air Source Heat Pump In Winter?
Using an air-source heat pump in winter offers numerous benefits, including enhanced energy efficiency, significant cost savings, a reduced environmental footprint, and consistent heating performance throughout the season.
Energy Efficiency
Air source heat pumps are known for their utilisation of ambient air as a heat source, extracting heat even in colder conditions. The coefficient performance, or COP (Coefficient Of Performance), measures the ratio of heat output to electricity input. Typically, air source heat pumps have a COP ranging from 2.5 to 4, indicating how efficiently they can provide heat. It is important to note that as the temperature drops significantly, the efficiency of these heat pumps may decrease, causing them to work harder and consume more electricity for heating purposes.
Cost Savings
One of the most appealing benefits of air-source heat pumps is the potential for significant cost savings on home heating bills, especially when compared to traditional gas heating systems.
When considering the energy consumption of air-source heat pumps versus gas heating systems, the difference can be quite striking. Air source heat pumps are known for their high energy efficiency, converting every unit of electricity into multiple units of heat. On the other hand, gas heating systems often have lower efficiency rates and can result in higher energy costs over time.
The initial installation cost of an air source heat pump may be higher than a gas heating system, but the long-term savings on energy bills make it a worthwhile investment. This makes air-source heat pumps a more sustainable and cost-effective choice for homeowners looking to reduce their energy expenses.
Environmentally Friendly
Air source heat pumps are an environmentally friendly heating option, reducing your home’s carbon footprint by using efficient heat transfer processes and consuming less energy compared to conventional heating methods.
By harnessing renewable ambient air temperature, air source heat pumps operate with high efficiency, reducing the reliance on traditional fossil fuels, and thereby cutting down carbon emissions. The minimal energy consumption associated with these systems makes them a sustainable heating solution for eco-conscious homes. The installation of air-source heat pumps leads to a significant decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental conservation. The long-term positive impact on the environment is substantial, aligning with the global shift towards greener technologies.
Consistent Heating
Air source heat pumps provide consistent heating throughout the winter, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature efficiently, regardless of outdoor weather conditions.
One of the key reasons behind their reliable performance is the technology used, which allows them to extract heat from the outside air even when temperatures drop below freezing. This means that air-source heat pumps can consistently deliver warmth to your space, making them a dependable heating solution for cold winter days.

What Are The Factors That Affect The Performance Of An Air Source Heat Pump In Winter?
Several factors can affect the performance of an air source heat pump in winter, including outdoor temperature, the level of home insulation, and the size and type of the heat pump unit installed.
Temperature
The performance of air source heat pumps is heavily influenced by outdoor temperature, with efficiency changes becoming more noticeable in colder weather as the unit works harder to extract heat.
As the temperature drops, the heat pump has to put in extra effort to draw heat from the outside air, leading to a decrease in efficiency. This strain on the system can result in reduced heating capacity and longer heating cycles, affecting overall performance.
Optimal temperature ranges for air source heat pumps are generally between 25 to 50 degrees Fahrenheit. Outside of this range, the unit may struggle to maintain desired indoor temperatures and operate efficiently.
Insulation
Proper insulation in your home is crucial for maximising the efficiency of air source heat pumps, as it helps retain the heat generated and reduces the workload on the heating system.
When your home is well-insulated, it creates a barrier that prevents heat loss, allowing the heat pump to operate more effectively. This means that the system has to work less to maintain a comfortable temperature, which can lead to lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact.
In addition, quality insulation helps in maintaining a consistent temperature throughout your home, avoiding draughts and cold spots. This even distribution of heat contributes to a more comfortable living environment and ensures that the heat pump operates at its peak performance.
Size And Type Of Heat Pump
The size and type of heat pump you choose significantly impact its performance, with larger and more advanced models often proving to be the most efficient in various weather conditions.
When considering the size of a heat pump, it’s essential to match it to the square footage of the area you intend to heat or cool. Oversized units can lead to inefficiencies due to short cycling, while undersized ones struggle to maintain the desired temperature.
- The type of heat pump also matters.
- Air-source heat pumps are the most common and work well in moderate climates.
- Geothermal heat pumps are more efficient but require a larger upfront investment.
- Ultimately, selecting the right size and type of heat pump ensures optimal performance and energy savings in the long run.
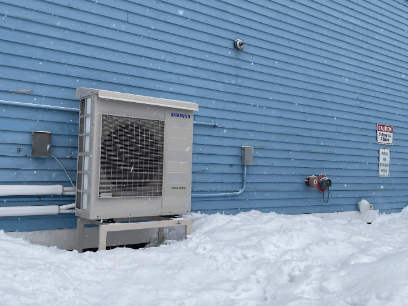
How To Maintain And Troubleshoot An Air Source Heat Pump In Winter?
Maintaining and troubleshooting an air source heat pump during winter is essential for ensuring its efficient operation, involving regular maintenance routines, identifying and resolving common issues, and seeking professional help when necessary.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your air source heat pump during winter is vital to ensure it runs efficiently, including tasks such as cleaning filters, checking for blockages, and inspecting components for wear and tear.
To keep your heat pump in top condition during the colder months, you should also regularly clean the outdoor unit to remove debris and ensure proper airflow. This helps optimise performance and energy efficiency.
Checking the refrigerant levels and coils, lubricating moving parts, and calibrating the thermostat are crucial tasks. Carrying out these maintenance activities can extend the lifespan of your heat pump and prevent costly repairs down the line.
Remember, a well-maintained heat pump not only keeps you comfortable but also saves you money on utility bills.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with air source heat pumps in winter include frost build-up, reduced efficiency, and unusual noises, all of which can be troubleshot with basic checks and maintenance techniques.
One of the most common problems that heat pumps encounter during the colder months is the accumulation of frost on the outdoor unit. This can hamper the heat exchange process and affect the overall performance of the system. To address this, periodic defrosting is essential by either manually melting the ice or using a specialised defrost mode if available.
Another issue that may arise is reduced efficiency, leading to higher energy bills and inadequate heating. This could be caused by a dirty air filter, improper thermostat settings, or even low refrigerant levels. Regular filter replacements, adjusting the settings, and scheduling professional refrigerant checks can help maintain the system’s efficiency.
Professional Help
When facing serious issues with your air source heat pump in winter, seeking professional help is crucial to ensure the system’s efficiency and longevity, preventing costly repairs and potential system failures.
Professional assistance plays a key role in diagnosing and fixing complicated problems that may arise with your heat pump, especially during the winter months when the system is heavily relied upon. Regular servicing by experienced technicians can also enhance the overall performance of the unit, optimising its energy efficiency and reducing utility bills. It’s essential to remember that neglecting proper maintenance can lead to significant issues down the line, affecting both the comfort of your home and your wallet. Don’t underestimate the value of expert intervention when it comes to your heating system.